Facts about Avian Flu
UPDATES (as of February 12, 2025)
- Pennsylvania Department of Health guidance document, BIRD FLU GUIDANCE FOR HUNTERS
- Pennsylvania Department of Health, Health Advisory Notice (HAN) 2025-784-02-07-Flu.pdf - The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released updated recommendations to accelerate influenza A subtyping in hospitalized patients to identify and support care (CDC -HAN - 00520). Hospitals are urged to subtype all influenza A positive specimens collected from hospitalized patients, prioritizing ICU patients. Subtyping should be done as soon as possible, ideally within 24 hours of admission.
Facts About Avian Flu
1. What is Avian Flu?
Avian flu, also called H5N1 influenza or bird flu, is a disease caused by certain flu viruses that usually spreads between birds, not people. Infected birds can spread the virus through their mucous, saliva or feces. People rarely get avian flu, but when they do, it is most often through direct unprotected contact (no gloves, protective wear, facemasks, respirators, or eye protection) with infected birds.
People can become infected by breathing virus in droplets in the air or possibly dust, or by touching surfaces contaminated with infected bird mucous, saliva or feces and then touching their eyes, mouth, or nose.
Avian flu viruses are very different from human seasonal influenza viruses. They have the potential to cause a pandemic in people if they were to gain the ability to more easily infect and spread efficiently between people because people have little pre-existing immunity to these viruses. Currently, no avian influenza A viruses, including avian influenza A(H5N1), have gained the ability to spread easily and sustainably among people.
2. How is Avian Flu Spread?
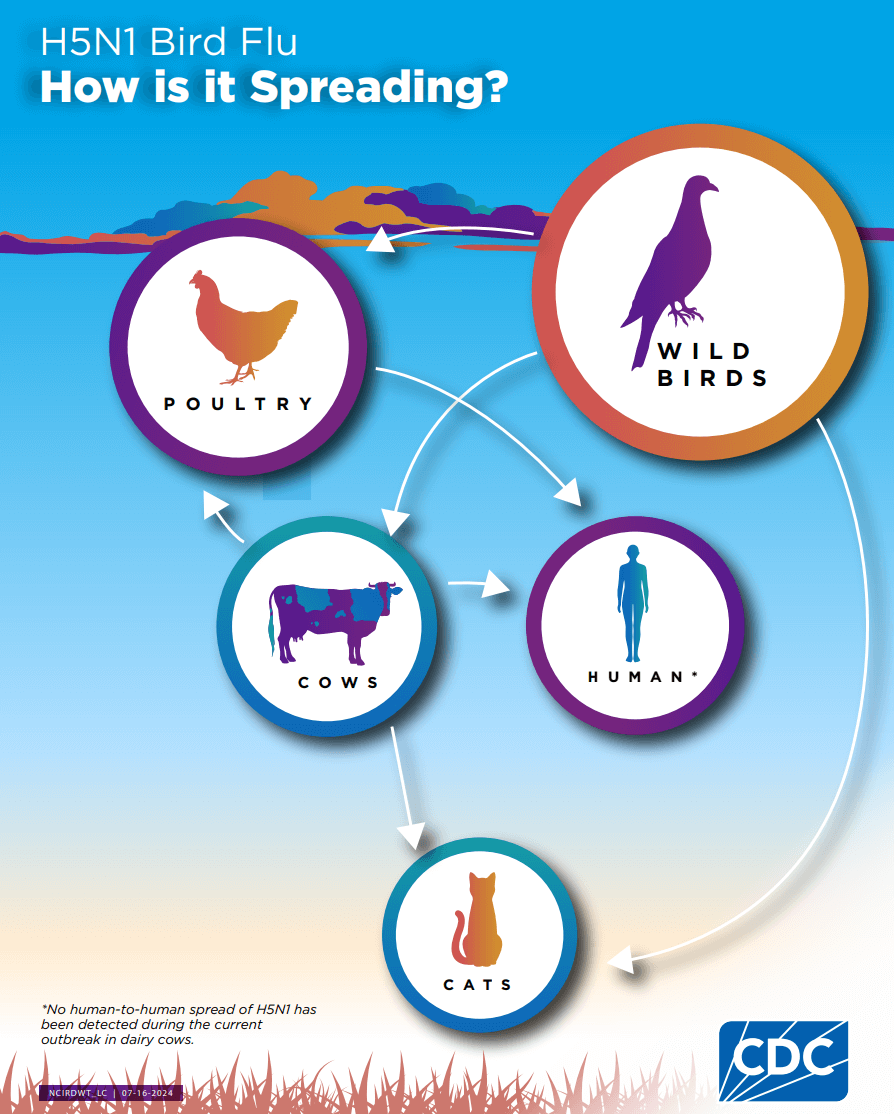
3. Can People Catch Avian Flu?
Although avian flu A viruses usually do not infect people, there have been some rare cases of human infection with these viruses.
4. Is There a Test For Avian Flu?
People can test for human seasonal influenza A virus using standard respiratory panels at your health professionals’ office or by using a take home kit from one of DCHD’s free public health kiosks. However, specialized further testing is needed to confirm if avian flu. This extra step is taken if you have a relevant exposure history.
5. What are the Symptoms of Avian Flu in People?
Illness in people from avian flu infections have ranged in severity from no symptoms or mild illness to severe disease that resulted in death.
Mild signs and symptoms of bird flu in people may include:
- eye redness and irritation (conjunctivitis)
- mild fever
- cough
- sore throat
- runny or stuff nose
- muscle or body aches
- headaches
- fatigue
Eye redness has been the predominant symptom among recent U.S. cases of bird flu infection. Less common symptoms include diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting.
Signs and symptoms of moderate to severe disease from bird flu in people may include:
- high fever or other symptoms listed above that limit or prevent usual activity
- shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- altered consciousness
- seizures
6. Is there a Vaccine for Avian Flu?
There are vaccines for avian flu, but they are not widely available for people.
While getting a seasonal flu vaccine only prevents seasonal flu and will not protect against avian flu, it is important that people who may have frequent exposure to infected or potentially infected birds or other animals get a seasonal flu vaccine. This is because it can reduce the prevalence and severity of seasonal flu and might reduce the very rare risk of coinfection with a human seasonal virus and an avian virus at the same time.
7. What Can I Do to Prevent Catching Avian Flu?
People should avoid direct contact with wild birds and other animals infected with or suspected to be infected with avian influenza A viruses.
If you must have direct/close contact with infected or potentially infected birds or other animals, wear recommended personal protective equipment (PPE). Wild birds can be infected with avian flu viruses even if they don't look sick.
- Do not touch surfaces or materials (e.g., animal litter or bedding material) contaminated with saliva, mucous, or animal feces from wild or domestic birds or other animals with confirmed or suspected avian flu infection.
- Do not touch or consume raw milk or raw milk products, especially from animals with confirmed or suspected avian flu infection.
8. Can I Consume Poultry, Eggs, and Dairy during an Outbreak?
Yes.
- Cook poultry, eggs, and beef to a safe internal temperature to kill bacteria and viruses.
- Choosing pasteurized milk and products made with pasteurized milk is the best way to keep you and your family safe.
- Unpasteurized (raw) milk and products made from raw milk, including soft cheese, ice cream, and yogurt, can be contaminated with germs that can cause serious illness, hospitalization, or death.
- Pasteurization kills bacteria and viruses, like avian influenza A viruses, in milk.
9. What Do I Do if I Suspect I've Been Exposed to Avian Flu?
- CDC has information available for different groups of people who become sick after contact with infected birds: https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/media/pdfs/2024/07/Bird-Flu-Exposure-Handout.pdf
- People who become sick within 10 days of their exposure to infected or potentially infected birds or other animals should isolate at home away from their household members and should not go to work or school until they are proven not to have avian flu infection. Call DCHD’s wellness line immediately if you develop any illness signs or symptoms during the 10-day observation period after an exposure to infected or potentially infected birds.
10. How Can I Protect My Pets from Avian Flu?
Don't allow your pets to contact sick or dead birds, their feces or litter, or any surface or water source (e.g., ponds, waterers, buckets, pans, troughs) that might be contaminated with their saliva, feces, or any other bodily fluids.
11. What if I Have a Backyard Poultry Flock?
People who have backyard or hobbyist flocks should report sick birds or other animals or unusual bird or other animal deaths to the state or the federal government, either through their state veterinarian or by calling USDA's toll-free number at 1-866-536-7593. You are the best protection to keep your birds safe from disease; information on protecting your backyard flocks is available on USDA's APHIS website at https://www.aphis.usda.gov/livestock-poultry-disease/avian/defend-the-flock.
For more information and assistance, the Delaware County Health Department Wellness Line is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. In addition to responding to phone calls, the Wellness Line also responds to email inquiries.
Phone: (484) 276-2100 (Available 24/7)
Email: DelcoWellness@co.delaware.pa.us
